Multimedia product designers must provide high quality audio effects, including high output speaker modes. These places require a system of audio amplifiers.
The efficiency of a linear amplifier is 50%, so a slight increase in output power leads to a large increase in current loss and excessive heat dissipation, resulting in the need for a large heat sink. In car audio systems, space and cost are invaluable, so the cost of these heat dissipation factors is quite expensive.
However, Class D amplifiers have the highest power consumption when the output power is at its maximum. When playing music, the amplifier reaches a peak output power for a short period of time, thus reducing the RMS output power. This feature makes it possible to use a much smaller heat sink than a linear amplifier, making it a great advantage for automotive OEMs. The main unit can provide additional output channels without the need for expensive external amplifiers. In addition, there is a relatively high sound quality, the cost of the package and heat generator is minimized, and there is savings in the power supply.
The heat sink of the Class D amplifier can be safely sized according to the half-peak of the output power. However, designers still have to determine the exact size, cost and application of the heat sink. The PCB design of the amplifier can also be used to reduce heat dissipation. Copper pads with large scale integrated circuits and all the widest PC traces connected to the IC minimize power consumption.
Class D output transistors operate in a switching mode from full "on" to full "off", which takes very little time in the linear region, so the power for heat loss is very small. If the resistance of the transistors is low, the voltage drop across them is small, which further reduces power consumption.
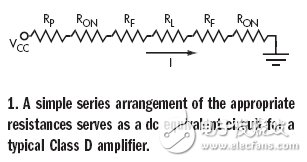
The DC equivalent circuit of a typical Class D amplifier with two transistors "on" is just a series of series resistors: RON, the output conduction loss of each transistor; RP, metal interconnects, lead structures, and PC board traces. Resistance; PL, load resistance (Figure 1). Another power generation is the switching delay in the output resistor (Figure 2). The efficiency of the entire system can be estimated as follows:
![]()
For example, suppose a dual-channel Class D amplifier that drives a 4Ω woofer operates at 60°C with 90% efficiency at full power, does not require a 14V DC power supply, and has a 5°/W IC junction resistance ( ΘJA). For a sinusoidal signal, the limit of the peak current output is:
![]()
This is in line with PLOAD PEAK = "I2PEAKRL" = 49W / channel output peak power, and PLOAD RMS = "PLOAD" PEAK / 2 = 24.5W / channel RMS output power. Adopt the efficiency formula:
![]()
The total heat dissipation is about 6W.
The highest junction temperature is not directly related to the performance of the amplifier. However, the junction temperature is significant for determining the size of the heat sink because higher TJs can handle higher power consumption. The temperature of the mold is TJ = TA + PDISS & TImes; Θ JA = 90 ° C, which is less than the maximum junction temperature of the device of 150 ° C.
In practical examples of using music signals, the designer must consider the maximum amplitude (crest factor) of the average of the signals. A typical music signal has a crest factor of 3 to 10. In decibels, it is 10~20dB [PdB=20log10(VPEAK/VREF)]. Therefore, in order to make the largest part of the music signal pass without distortion, the amplifier needs 10-20 dB of dynamic space compared to the general power output.
When the Class D amplifier operates at 14V, a 98W peak can occur. Convert to decibel is:

Subtract the limit of the crest factor to get the average sound level of the undistorted output:

Convert to RMS output power:

When the PPEAK is 98W and the RMS output power is 955mW, the total power consumption is 0.2W and the maximum junction temperature is 61°C. When the RMS output power is 10W, the total power consumption is 2.2W and the maximum junction temperature is 71°C. Therefore, the maximum power consumption of an undistorted audio CD signal occurs when the average sound is 4 dB.
These examples show that sinusoidal signals consume more power than true audio signals. Therefore, the sinusoidal signal can be used as a load for extreme thermal testing, causing the amplifier to turn off due to heat.
LED Flood Light made by aluminum alloy. Surface coating by special technology or anodizing aluminum process, impact resistant,sturdy and durable features. Fins design of heat,rational utilization cross-ventilation to improve products stability and working life.
SMD LED Flood Light, the Waterproof level of LED Flood Light is IP65.IP66.IP67.All of them applied in commercial and residential.
LED Flood Light
LED Flood Light,High Power LED Floodlight,LED Outdoor Flood Lighting,Explosion Proof LED Flood Light
Wenzhou Korlen Electric Appliances Co., Ltd. , https://www.korlenelectric.com