In today's world's energy shortage and increasingly serious environmental pollution, the full development and utilization of solar energy is one of the energy strategies actively implemented by governments around the world. The application of solar LED lighting systems is in line with the development trend of this strategic decision. However, the development of LED lighting systems has been largely affected by thermal issues.
For LED lighting systems, LEDs can only convert a small amount of electrical energy into light energy during operation, and most of the energy is converted into heat. As the power of the LED increases, the amount of heat is increased. If the heat dissipation problem is not solved well, the heat is concentrated in the chip having a small size, so that the internal temperature of the chip is getting higher and higher. When the temperature rises, it will cause the following effects [1]: (1) the working voltage is reduced; the light intensity is reduced; the wavelength of the light is longer. (2) Reduce the efficiency of the LED driver, damage the life of the magnetic component and the output capacitor, and reduce the reliability of the LED driver. (3) Reduce the life of the LED and accelerate the light decay of the LED. The heat dissipation problem of LED lighting systems has become a major obstacle to the development of this technology. At present, the main methods used in solving the heat dissipation problem of the LED lighting system are: adjusting the spacing of the LEDs; reasonably increasing the distance between the LED and the metal core printed board; punching mode; installing a fan. These methods are affected by many objective conditions in practical applications, and the heat dissipation effect is not very satisfactory.
Semiconductor refrigeration, also known as thermoelectric refrigeration [2], is the use of the Peltier effect of semiconductor materials. When the direct current is passed through a galvanic couple of two different semiconductor materials in series, heat can be absorbed and heat can be released at both ends of the galvanic couple, and the purpose of cooling can be achieved. It is a refrigeration technology that produces negative thermal resistance, which is characterized by no moving parts and high reliability. The use of semiconductor refrigeration to solve the heat dissipation problem of LED lighting systems has high practical value.
1. The working principle of semiconductor refrigeration
In 1934, the Frenchman Peltier discovered that when the current flows through the junction formed by two different conductors, it will generate exothermic and endothermic phenomena. The exotherm or endotherm is determined by the magnitude of the current.
Q=aTI
In the above formula: Q is exothermic or endothermic power; a is temperature difference electromotive force rate; T is cold junction temperature; I is working current.
Based on the Peltier effect principle, Peltier effect cooling is also called temperature difference cooling. The main principle of semiconductor refrigeration technology is based on the Peltier effect. Semiconductor refrigeration is based on the characteristics of thermoelectric effect technology. It uses special semiconductor material thermopile to cool, which can convert electric energy directly into heat energy with high efficiency. At present, the semiconductor materials used in refrigerators are mainly bismuth telluride [3]. The addition of impurities is specially treated to form N-type or P-type semiconductor temperature difference components. Its working characteristic is that one side of the cooling side is heated.
According to quantum theory, metal and semiconductor materials have different energy levels, different contact potential differences, and different load bodies. As shown in Figure 1, the P-type and N-type semiconductors are connected by a metal plate, and the other end is formed by a metal plate to form a circuit in the figure. When the electric key k is closed, the current in the figure passes through the PN junction, and thus The Peltier cooling effect is formed at the upper end of the semiconductor and the metal plate, and the Peltier effect is formed at the lower end [4].
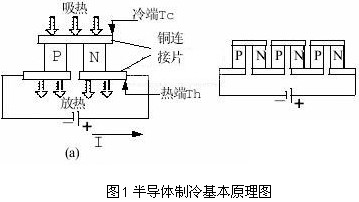
2. Design of semiconductor refrigeration system
2.1 semiconductor refrigeration system composition
In the semiconductor refrigeration system, the cooling sheet adopts the TEC1-12703 type thermoelectric cooling assembly. According to the characteristics of the lighting system, the plexiglass with visibility, toughness and high temperature resistance is selected as the refrigerator wall. In order to better solve the heat dissipation problem of the solar LED lighting system, the controller is used to effectively control the semiconductor refrigeration system.