There are typically three common methods for grounding a voltage transformer, each serving a specific purpose in the electrical system:
- Grounding the primary side neutral point
- Grounding the secondary side coil
- Grounding the transformer core
The effects of these groundings vary significantly, and understanding them is essential for proper system design and safety. Let's explore each one in detail.
1) Grounding the Primary Side Neutral Point
In a star-connected configuration using three single-phase voltage transformers, the primary side neutral point must be grounded. This setup is commonly used in power systems where accurate voltage measurement and relay protection are required. As shown in the diagram below, grounding the primary neutral ensures that zero-sequence currents can flow during a single-phase ground fault.
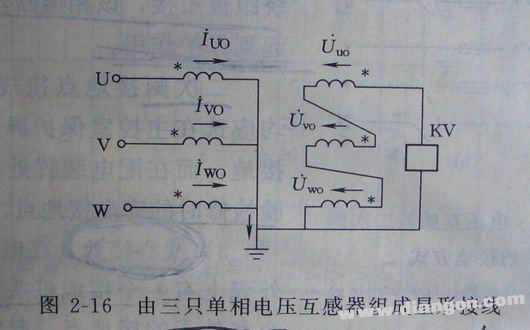
If the primary neutral is not grounded, no path exists for zero-sequence current on the primary side. As a result, the secondary side open delta coil will not induce a zero-sequence voltage, and the protective relay (KV) will not activate, leading to an inability to detect ground faults.
This principle also applies to three-phase five-column voltage transformers, where the primary side neutral must still be grounded. However, in a VV-connected system using two single-phase voltage transformers, the primary side should not be grounded. Instead, the secondary neutral point should be grounded to avoid direct phase-to-ground connections, as illustrated below.
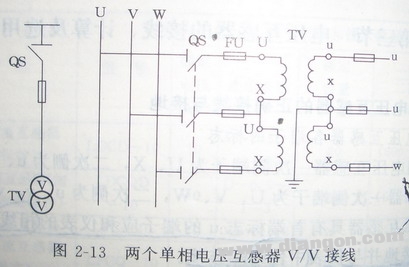
2) Grounding the Secondary Side
It is crucial to have at least one grounding point on the secondary side of the voltage transformer. This is primarily for safety reasons. If the insulation between the primary and secondary windings fails, high voltage from the primary side could be transferred to the secondary, posing serious risks to personnel and equipment. Grounding the secondary side helps prevent such hazards.
Additionally, grounding the secondary side allows the system to provide phase voltages to insulation monitoring devices. There are generally two types of secondary grounding: neutral grounding and V-phase grounding. The choice depends on the specific requirements of the system, such as relay protection settings.
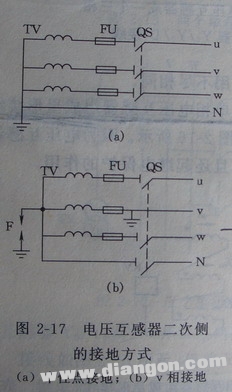
When the V-phase is grounded, the neutral point cannot be directly grounded. To prevent high voltage from penetrating the secondary side due to insulation failure, the secondary neutral is usually grounded through a protective gap. In case of a breakdown, the gap will short-circuit the V-phase winding, causing the fuse to blow and protecting the system.
According to industry standards, the secondary grounding point should be located in the main control room’s protection panel via a terminal block. Only a temporary grounding point may be placed at the power distribution device during testing or maintenance.
3) Grounding the Transformer Core
Every voltage transformer has a grounding stud on its housing, which serves as a safety grounding point for both the core and the outer casing. This connection is vital for preventing electric shocks and ensuring overall system stability.
Proper grounding of all components—primary, secondary, and core—is fundamental to the safe and efficient operation of voltage transformers in power systems. Understanding these grounding techniques helps engineers and technicians make informed decisions when designing, installing, and maintaining electrical infrastructure.
The SUNKET All-Black Series Modules, with its true black and consistent color, can be perfectly integrated with the building (the villa effect is better), and enhance the aesthetic effect of the overall building.
The Solar Cell adopts nano-scale black silicon texturing technology, which reduces the reflectivity of the cell, improves the utilization rate of sunlight, and improves the cell efficiency and module power.
The SUNKET All-Black Series Module also integrates various technologies such as Half-cut and MBB to achieve higher power output and reliability. Using half-cut technology, reducing resistance loss and improving power output; using MBB technology can shorten the current transmission distance, reduce the internal resistance loss of the cell, and bring more power output to customers. At the same time, the half-cut technology can also reduce the hot spot temperature of the module, and the MBB technology has better anti-cracking ability, which can improve the reliability of the module and meet the needs of high safety performance of the roof.
Mono Panel,Silicon Solar Panels,Mono Solar Panel Price,All Black Solar Panel
Wuxi Sunket New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.sunketsolar.com