MPEG-2 compression encoder is a front-end device that converts analog TV video and audio signals to MPEG-2 compression encoding and outputs real-time TS streams.It is suitable for various applications such as digital TV transmission or front-end source encoding, conference TV, and distance education. An advanced encoder not only has a DVB interface, but should also be equipped with a telecommunications interface, so that the device can be easily applied in networks such as HFC networks, microwave MMDS or 8GHZ systems, SDH or PDH, as shown in Figure 1.
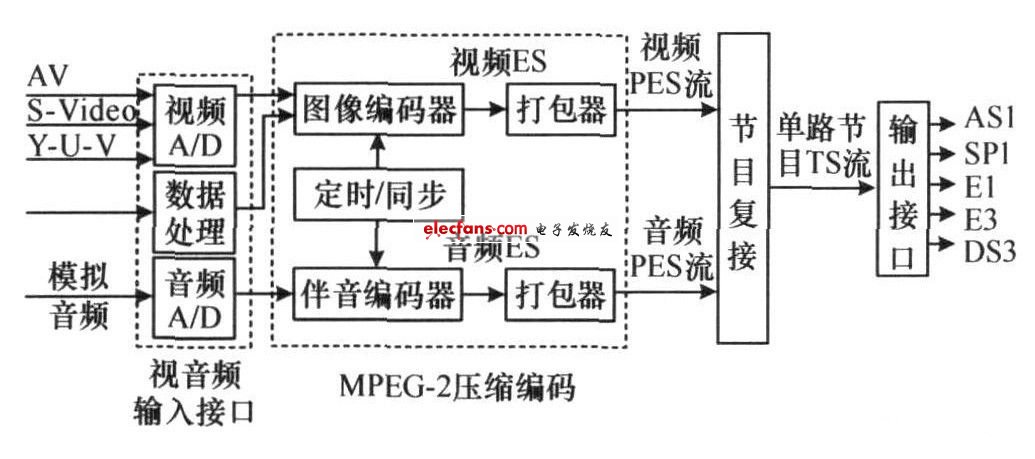
Figure 1 Block diagram of the encoder.
MPEG-2 video coding system and key technologies
The principle of MPEG-2 image compression is to use two characteristics in the image: spatial correlation and temporal correlation. Any scene in a frame of image is composed of several pixels, so a pixel usually has a certain relationship with some pixels around it in brightness and chromaticity. This relationship is called spatial correlation; a program A plot in is often composed of a sequence of images composed of several consecutive images. There is also a certain relationship between the front and back frames of an image sequence. This relationship is called time correlation. These two correlations make a lot of redundant information in the image. If we can remove these redundant information and only retain a small amount of non-related information for transmission, we can greatly save the transmission band, and the receiver uses these non-related information, According to a certain decoding algorithm, the original image can be restored on the premise of ensuring a certain image quality. A good compression coding scheme is to remove the redundant information in the image to the greatest extent.
The encoded images in MPEG-2 are divided into 3 categories, called I frame, P frame and B frame.
The I-frame image adopts the intra-frame coding method, that is, only the spatial correlation in a single frame image is used, and the temporal correlation is not used. I-frames are mainly used for receiver initialization, channel acquisition, and program switching and insertion. I-frame images have relatively low compression ratios. I-frame images periodically appear in the image sequence, and the frequency of appearance can be selected by the encoder.
P-frame and B-frame images use inter-frame coding, that is, to use spatial and temporal correlation at the same time. P-frame images only use forward time prediction, which can improve compression efficiency and image quality. The P-frame image may contain an intra-coded part, that is, each macro block in the P-frame may be forward predicted or may be intra-coded. B-frame images use bidirectional time prediction, which can greatly increase the compression factor. It is worth noting that, because the B frame image uses the future frame as a reference, the transmission order and display order of the image frames in the MPEG-2 coded code stream are different.
MPEG-2's code stream is divided into 6 levels. In order to better represent the encoded data, MPEG-2 specifies a hierarchical structure with syntax, which is divided into 6 layers, from top to bottom are: image sequence layer, group of pictures (GOP), image, macroblock, macro Blocks, blocks. The main applications of the MPEG-2 standard are as follows: preservation of video and audio data; non-linear editing systems and non-linear editing networks; microwave, satellite, and optical cable transmission; broadcast of TV programs. In the all-digital TV technology, there are two key coding technologies, namely source coding and channel coding. They use MPEG-2 technology. The main task of source coding is to solve the compression and preservation of image signals. Channel coding The main task is to solve the problem of image signal transmission. The data volume of the image signal is large. If it is not compressed, the digital TV signal cannot be transmitted in real time, and the main method of compression is to remove the redundant signal. The so-called redundant signal refers to the extra parts that are not related to information or have little effect on the image quality. This is the principle of MPEG-2 image compression.
(1) Spatial redundancy. An image is composed of hundreds of thousands of pixels, and there are great similarities (or correlations) between adjacent two or even a few pixels.When transmitting, there will be continuous transmission of many identical data, which is called Spatial redundancy, using a certain coding method (such as orthogonal transform coding), to remove redundant information in space, reduce transmission and recording bit rate.
(2) Time redundancy. TV images also have a strong temporal correlation. For images of 25 frames / s, the difference between the previous frame image and the next frame image is usually small, and most of the screen content is the same, which indicates that two adjacent images The correlation is very large, and when the images are far apart, the correlation of the images gradually decreases, and such highly correlated images are generally regular when changing, that is to say, each image The changes are predictable. Using the temporal redundancy feature of the image to remove the redundant information of the image signal in time can also reduce the transmission and recording bit rate.
(3) Statistical redundancy. After digitizing the image and sound signals, certain statistical laws are followed. For example, under the image prediction coding system, the predicted value of the current pixel signal is predicted by the values ​​of the first few adjacent pixels or the time value of the pixel in the previous segment. According to the spatial correlation and temporal correlation of the image, it is known that the probability of occurrence of a signal with a small prediction error is large, and on the contrary, the probability of appearance is small. Using the statistical coding method, short codes are used for small error signal values ​​with a large probability of occurrence, and long codes are used for large error signal values ​​with a small probability of occurrence, so that statistically redundant information of the signal is removed.
(4) Perception redundancy. Human audiovisual organs have certain insensitivities. Perceptual redundancy refers to video and audio signals that are insensitive or unattainable to people's visual and auditory resolution. When these insignificant information are given large distortions, people will not obviously feel the degradation of image and sound quality. , Even unaware. Therefore, when encoding, different content can be divided into long code and short code, which is called doing something and not doing something, so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the code rate.
For more encoder knowledge, please visit http: //
Seat Tube Battery,Inner Seat Tube Battery,Seat Battery Packs,Electric Bike Battery 24V
Changxing Deli Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.delipowers.com