How much computer memory is enough? Now look, 8GB starting 16GB is just fine. What about speed? DDR4 2666 is undoubtedly ideal. But do you know that although memory seems to be much faster than hard disks, it is still very slow for CPUs. When the CPU and memory exchange data, the CPU's internal cache is the key to the key, today Xiao Bian will share with you about the CPU cache of those things.

CPU cache to use?
Now the memory on a computer, even Intel's Aspiren memory, is not as fast as the cache in the CPU. Moreover, the size and design of the cache are also one of the important performance indicators of the CPU.
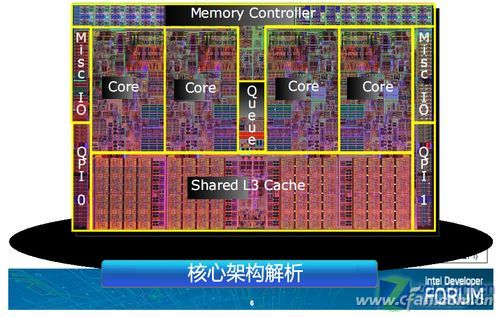
The first is the cache operating frequency in the CPU - how much the CPU frequency is the operating frequency of the cache, and there is a bottleneck in the I / O output, because it is inside the CPU. Therefore, the work efficiency of the CPU cache far exceeds the memory and the hard disk, and it can be said that it is not at a single level.
So how does the cache work? When the CPU wants to read data and perform calculations, it first looks for the required data from the internal cache, and if so, it can deliver the CPU at the fastest speed in the shortest time. However, if it is not found, the CPU will ask "required" to read from the memory through the cache, and then return to the CPU to calculate. At the same time, the data in which this data is located is also buffered, so that future reads of the entire block of data can be performed from the cache without calling the memory.
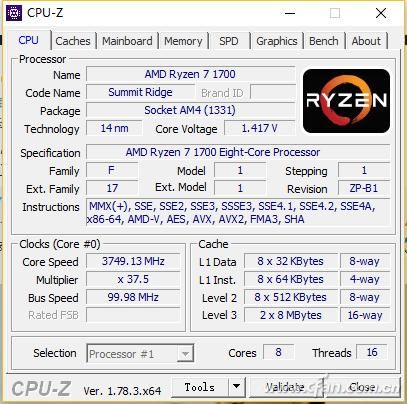
Why do you still need three levels of cache?
CPU-CPU cache-memory, which is roughly the working state. However, in order to further optimize the "scheduling" of the data, the cache of the CPU is also divided into several levels for optimizing the throughput and temporary storage of data and improving the execution efficiency.
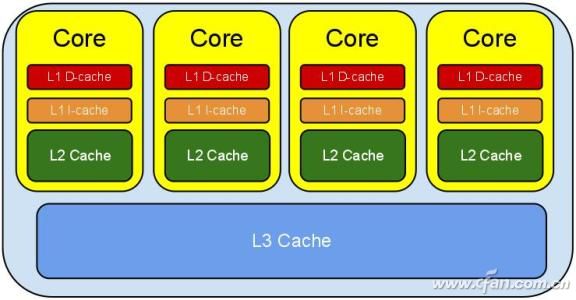
L1 Cache L1 cache
The first-level cache is the first-level cache of the CPU, and its main task is to cache data and cache instructions. L1 tells that the cache capacity and structure have a great impact on CPU performance, but due to its complex structure, considering the cost and other factors, the general CPU's L1 cache can also achieve about 256KB.
L2 Cache L2 cache
The second-level cache is the second-level cache of the CPU. The capacity of the second-level cache directly affects the CPU performance. The principle is that the bigger the better. And it is followed by the core, such as the 8 generation Core i7 8700, 6 cores each have 256KB of secondary cache, which is exclusive to each core, so that the total reached 1.5MB.
L3 Cache L3 cache
The three-level cache was originally a server-level CPU and was gradually decentralized to a home-level CPU. The role of the third-level cache is to further reduce the memory delay, while improving the performance of the massive amount of data calculation, which has a direct impact on the game! Unlike the L2 cache, the L3 cache is shared by the core, and the capacity can be very large.
The frequency of the CPU and the number of cores are the keys that directly affect performance. However, how to make the CPU smarter and more efficient to perform computational tasks, the role of the cache is crucial. In addition, both the Intel and AMD, the CPU's three-level cache capacity is increasing, this is mainly to enhance the user, especially the game player's use of feelings.

Wall Switch And Socket,Wireless Wall Switch,Decora Light Switch,Push Button Light Switch
ZHEJIANG HUAYAN ELECTRIC CO.,LTD , https://www.huayanelectric.com